What is a digital twin?
A digital twin is a dynamic digital representation of a physical system, plant, or equipment that harmonizes data, analytics, and insights from multiple sources. By connecting real-time operational data, engineering models, documents, and historical information in a single platform, it provides context-rich, actionable intelligence. All together, these elements provide a comprehensive view of how an asset performs and interacts within its environment. Users can visualize performance, monitor assets, optimize processes, and make informed decisions faster.
How does a digital twin work?
A digital twin works by connecting a physical asset, system, or process to a digital model through real-time data streams, historical information, and analytics. Sensors and IoT devices feed operational data into the digital twin, while engineering models and data standards provide context and structure.
Advanced analytics, including AI and predictive algorithms, interpret the combined data to simulate performance, detect anomalies, and predict outcomes. Users can visualize insights through interactive dashboards, test scenarios virtually, and optimize operations without interrupting real-world processes.
Types of digital twins
There are no different types of digital twins. There is only one, single, flexible digital representation of assets, processes, and systems, designed to scale across any use case. By harmonizing real-time data, analytics, and operational insights in context, it enables organizations to optimize performance, reduce risk, and improve decision-making.
From individual equipment monitoring to process optimization and complex system management, the same digital twin platform adapts to meet specific business needs. For example, manufacturers can predict machine maintenance and minimize downtime, energy operators can optimize interconnected assets across networks, and automotive engineers can simulate performance to enhance product designs. This unified approach ensures consistency, accelerates time-to-value, and allows organizations to expand their digital twin footprint without creating new silos—unlocking insights across engineering, operations, and enterprise functions.
Advantages and benefits of digital twins
Digital twins provide a transformative approach to decision-making. Businesses can monitor performance and identify trends; stakeholders can visualize complex systems and simulate various scenarios. These real-time and predictive insights empower decision-makers across roles and locations to make smarter choices—and to make them faster.
By providing a comprehensive view of asset performance, digital twins enable organizations to optimize resource allocation and streamline processes. This not only reduces operational costs but also enhances productivity, allowing companies to focus on growth and innovation.
Digital twins also play a crucial role in predictive maintenance and risk reduction. By continuously analyzing data, they can anticipate and address potential failures before they occur. This minimizes downtime and extends the lifespan of equipment, ultimately reducing maintenance costs and risks associated with unexpected breakdowns.
History and evolution of digital twins
The origins of digital twin technology can be traced back to NASA in the early 2000s, where the concept was initially developed for space missions. Engineers needed a way to simulate and analyze the performance of spacecraft in real-time, leading to the creation of virtual models that mirrored their physical counterparts. This innovative idea laid the groundwork for what we now know as digital twins.
The term itself appeared for the first time, so far as we know, in 2002 in a presentation Michael Grieves gave to the University of Michigan. Since then, the technology has evolved dramatically and proliferated across other industries like manufacturing, healthcare, urban planning, and more. The rise of advanced simulation technologies and data analytics, which enable more complex and accurate models, has accelerated this evolution even further.
More recently, advances in the internet of things (IoT) and AI have begun to supercharge digital twin technology. IoT devices enable real-time data collection from physical assets, allowing digital twins to be continuously updated and refined. Meanwhile, AI algorithms enhance the predictive capabilities of digital twins, enabling businesses to foresee potential issues and optimize operations proactively. This integration of IoT and AI has transformed digital twins from static models into dynamic, intelligent systems, making them essential tools for modern enterprises.
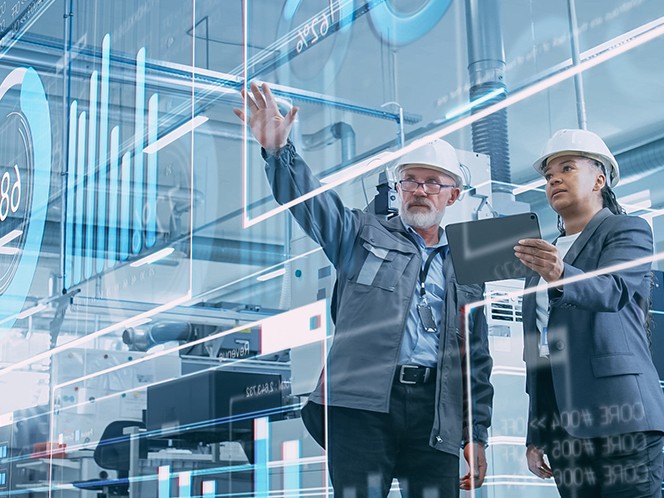

Digital twin applications across industries
Digital twins are rapidly transforming a wide range of industries. In manufacturing, digital twins enable companies to simulate processes, monitor equipment performance, and predict maintenance needs. Manufacturers can optimize production lines, reduce downtime, and improve product quality.
In healthcare and medical research, digital twins are making significant strides in personalizing patient care and advancing medical studies. By modeling individual patient data, healthcare professionals can simulate treatment outcomes, leading to more effective and tailored therapies. Researchers can even use digital twins to analyze disease progression, test new drugs, and streamline clinical trials.
Urban planning and smart cities also benefit from digital twin technology. City planners can create accurate digital replicas of urban environments to simulate traffic patterns, energy consumption, and resource allocation. This allows for better urban design and infrastructure management, more resilient, sustainable cities, and ultimately a better quality of life for residents.
Future trends in digital twin technology
Experts expect digital twin adoption will continue expand across sectors, and that its impact will continue to deepen. In manufacturing, companies are finding new ways to optimize production processes and reduce downtime even further. In healthcare, digital twins of patients could soon allow for personalized treatment plans. Urban planners may soon use digital twins to simulate entire city environments, enhancing infrastructure development and public safety.
Digital twins will also play an increasingly crucial role in monitoring environmental impact. By simulating the impact of different scenarios, industrial organizations can use resources more efficiently and reduce their carbon footprints more substantially. As the focus on sustainability increases, the integration of digital twin technology into environmental strategies will likely become a standard practice.
As digital twin technology continues to mature and evolve, it’s also becoming more affordable and accessible. Lower barriers to entry—combined with rapid advances in AI, IoT, and cloud computing—are making it easier than ever for organizations of all sizes to adopt and benefit from digital twin technology. The result is a future in which digital twins aren’t just more powerful; they’re pervasive.

Discover latest Digital Twin news and resources