Smart water: Harnessing IIoT and data analytics for sustainable water management
Posted: August 29, 2025

Today’s water management organizations face steep challenges. Much of the existing water management infrastructure—such as pipes, pumps, and treatment systems—is outdated and in need of upgrades.[1] Climate change is increasing the frequency of droughts and floods. In addition, stricter environmental regulations and rising sustainability expectations add pressure. Compounding these issues is a growing workforce gap, as experienced engineers and technicians retire and fewer skilled professionals enter the field. Although utilities collect vast amounts of operational data, many struggle to turn it into actionable insights for tasks like leak detection, predictive maintenance, and demand planning.
To meet these challenges, forward-thinking organizations are using IIoT and data-driven strategies to modernize water management, improve efficiency, and ensure reliable water access for communities today and in the future.

IIot technologies spur proactive solutions
IIoT technologies—combining sensors, data collection, and analytics—allow water utilities to monitor and optimize operations in real time. This includes tracking water quality, flow rates, and equipment performance, while supporting predictive maintenance, regulatory compliance, and remote operations. Companies are increasingly leveraging this kind of data for digital twin technology to gain insight in real time about water systems, enabling operators to better understand and optimize water use and distribution by simulating different scenarios.
To realize these benefits, utilities must make smart investments now and prioritize user-friendly, low-maintenance systems that suit limited IT staffing and resources.
By using a robust data infrastructure that integrates data across systems and enables advanced analytics, utilities gain a clearer more holistic understanding of their operations, which helps them:
- Streamline operations: Water utilities can leverage real-time data on consumption, supply, and distribution, tracking things like water quality and reservoir levels to optimize operations.
- Improve maintenance: Early detection of problems helps reduce downtime, water loss, and costs while boosting sustainability and service reliability. Real-time data and advanced analytics can help manage intermittent supply and provide real-time demand forecasting.
- Meet strict regulatory standards: An integrated digital platform with centralized data, prebuilt reporting tools, and secure storage streamlines compliance reporting and helps avoid penalties. Likewise, environmental agencies can use water quality data to track pollution, identify contamination sources, and take action to safeguard ecosystems and public health.
- Enhance water conservation efforts: IIoT can also enhance water conservation efforts by incorporating weather data, such as temperature and rainfall patterns, into forecasting and allocation models.
Below are three organizations that are harnessing industrial intelligence to manage and deliver safe, reliable drinking water—now and into the future.
Setting the model for smart urban water management
Sabesp, the sanitation company of the State of São Paulo, serves over 28 million people across 376 municipalities. Facing challenges such as high maintenance costs, hardware limitations, power outages, and unpredictable water demand, Sabesp needed a scalable solution to improve efficiency and reliability. In partnership with Stefanini IHM and AVEVA, Sabesp implemented a modern, distributed architecture built around AVEVA™ PI System™. This transition included migrating legacy systems, integrating over 3,000 pumps, and using more than 120,000 data tags and 27,000 assets for real-time monitoring and predictive modeling.
Centralized dashboards and intelligent alarms replaced manual data entry, enabling faster and more accurate responses to pump failures. The system also introduced real-time demand forecasting, using historical consumption data to dynamically adjust projections and better prepare for seasonal and weather-related fluctuations. This proactive approach allowed Sabesp to reduce operational costs, increase efficiency, and enhance service reliability.
By adopting a data-driven strategy, the company minimized the risk of water shortages, improved maintenance and planning, and ensured more efficient watershed management. In the São Paulo Metropolitan Region (RMSP) alone, this digital transformation led to a 1% reduction in water shortages, directly benefiting over 200,000 residents and setting the model for smart urban water management.
IoT-based water management platform to ensure water for every household
The Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM), under the banner of "Har Ghar Jal" (Water for Every Household), aims to ensure accessible, safe, and sustainable water supply across rural India. With a focus on quantity, quality, equitable distribution, sustainability, and affordability, the mission represents a major shift in water service delivery. Initially serving just over 32 million households, it now reaches over 153 million, transforming water access from communal collection points to direct in-home delivery.
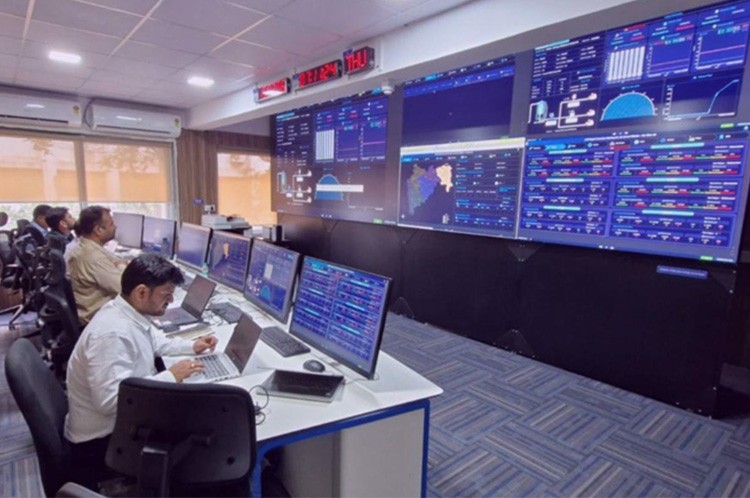 Easy visualizations allow JJM to monitor Maharashtra’s water supply network, from tracking real-time reservoir levels to water quality parameters like pH and turbidity.
Easy visualizations allow JJM to monitor Maharashtra’s water supply network, from tracking real-time reservoir levels to water quality parameters like pH and turbidity.
In Maharashtra, India’s third-largest state, the Jal Jeevan Mission implemented a robust IoT-based water management platform, integrating the AVEVA PI System with ESRI ArcGIS for real-time monitoring and visualization. This system provides end-to-end visibility into the rural water supply network—tracking service uptime, reservoir levels, pressure variations, and water quality parameters like pH, turbidity, and microbial content. AVEVA PI System enables predictive analytics to identify potential leaks, while ESRI’s mapping tools assist in pinpointing hotspots for rapid intervention. This integration helps address variability in water quality and supply, ensuring timely responses to anomalies, reducing water loss, and supporting operational decisions across a vast and complex infrastructure.
The platform has already been deployed across 9,000 villages in Maharashtra and is being scaled to 45,000 villages. By standardizing data from a wide array of sensors and devices across over 300,000 square kilometers, the system now delivers real-time insights that support safe, consistent, and equitable water delivery. It enables improved maintenance strategies, faster leak detection and repair, and more efficient resource management. These data-driven capabilities are helping India’s largest rural water utility initiative meet its ambitious goals of delivering clean and reliable drinking water to every household.
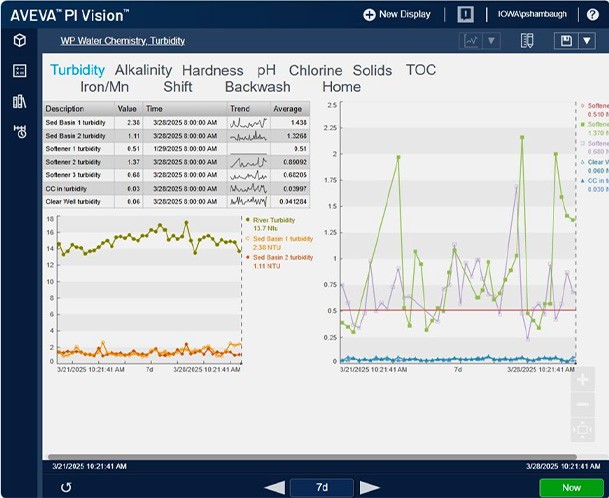 Dashboards using AVEVA™ PI Vision™ enable the University of Iowa to monitor water quality in real time.
Dashboards using AVEVA™ PI Vision™ enable the University of Iowa to monitor water quality in real time.
Data modernization at the University of Iowa’s water plant
The University of Iowa is one of the only colleges to have its own surface water treatment plant. Engie, an energy company, runs the utilities for the university, including managing the power plant, steam production, chilled water, and drinking water treatment plant. Until recently, the water plant at the University of Iowa stored its lab data in an aging Microsoft Access database from the 1990s. This database had numerous problems and limitations.
This data was used to calculate the water’s CT values—an equation of disinfectant concentration (C) multiplied by time (T) that tells operators if they have properly disinfected the water—an important metric for keeping drinking water safe for consumption.
Both ENGIE and the University of Iowa were already AVEVA PI System users, and there was a local team dedicated to its support, so the water plant group and the AVEVA team worked together to develop a platform based on AVEVA PI system to manage lab results.
Now, the water plant uses PI Manual Logger to input sample data, AVEVA™ PI Vision™ for visualization and sharing, and AVEVA™ PI DataLink™ for reporting in Excel. Complex calculations—like CT values, Langelier Saturation Index, and hydroxide alkalinity—are now automated through PI Asset Framework, using both real-time and lab data. The system not only streamlines data entry and analysis within a single platform, but also empowers operators, engineers, and managers with actionable, accurate insights.
Turning water management data into action
Over 2 billion people currently lack access to safe drinking water at home, with over half of the global population living in water-stressed areas.[2] The future of water management—and access to safe drinking water—depends on the ability to turn data into action. From urban megacities to rural villages and university campuses, these examples show that IIoT and advanced analytics are not just tools—they are lifelines for building more resilient, efficient, and equitable water systems. As climate pressures, aging infrastructure, and regulatory demands intensify, utilities that invest in smart, scalable data solutions today will be best equipped to deliver safe, sustainable water tomorrow.
[1] Renwick DV, Heinrich A, Weisman R, Arvanaghi H, Rotert K. (April 10, 2020). Potential Public Health Impacts of Deteriorating Distribution System Architecture. American Water Works Association. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7147732/
[2] Famiglietti, Jay. A Map of the Future of Water. Pew. https://www.pew.org/en/trend/archive/spring-2019/a-map-of-the-future-of-water
Related blog posts
Stay in the know: Keep up to date on the latest happenings around the industry.