The renewable energy transition is powered by industrial intelligence
Posted: July 29, 2025
Our current global energy systems account for about 75% of the world’s total greenhouse gas emissions. Specifically, these emissions come from burning fossil fuels for electricity and heat.[1] Though the transition to renewable energy is certainly underway, the pace of innovation sometimes seems sluggish—fossil fuels still make up 80% of the global energy supply.[2]
The good news is that organizations and utilities are stepping up. They are harnessing intelligent data platforms with AI-infused process simulation and predictive analytics to innovate sustainable energy—all while remaining resilient in tomorrow’s economy.
Harnessing industrial data solutions for renewable energy production
Renewable energy sources are often variable and intermittent, dependent on unpredictable factors such as weather, making grid integration a complex juggling act. Due to the variety of factors involved, producing and managing sustainable energy requires a different kind of approach. Real-time situational awareness, remote monitoring, and predictive analytics can help organizations succeed—and it all begins with data.
Whether you’re an energy company, a grid operator, or an organization looking to become a renewables prosumer, industrial data software can help you handle the complexity and variability of renewable energy sources. Through IoT devices, machine learning, advanced analytics, and AI, organizations can put their data to work for:
- Grid management: Renewable energy producers can anticipate, respond, and adapt to supply and demand in real time. Using historical and real-time weather, generation, and grid data, operators can predict fluctuations and anticipate shortfalls or surpluses accordingly.
- Asset optimization: Real-time asset monitoring using sensors and IoT devices allows producers to respond quickly to equipment failures as well as curtailment or ramp-up when needed.
- Process optimization: Dynamic process simulation enables producers to design, optimize, and operate complex energy systems more efficiently and cost-effectively. Advanced process simulation can simulate how intermittent renewable sources behave over time, explore different scenarios and test thermal and chemical processes, such as in green hydrogen production.
- Energy storage: Since renewable energy sources often entail the creation of a surplus that needs to be stored when demand is down, industrial data solutions can turn energy storage from a passive backup into a smart, dynamic asset—identifying optimal storage dispatch timing and helping match supply with demand more effectively. As production of renewable energy rises, battery storage becomes even more important, and tools that use machine learning and AI can help ensure batteries operate within ideal temperature and load ranges.
Take a look at how the following companies are innovating renewable energy production solutions by harnessing their industrial data. From real-time asset monitoring to the use of generative AI for intelligent energy dispatch, these organizations are taking big leaps forward in the renewable energy transition.
Brazil’s energy operator avoids $11.4M USD in losses
The National Electric System Operator (ONS) of Brazil supplies electricity to all of Brazil, with 92% of its energy load made up of renewable energy. ONS uses four main types of energy sources: hydro, thermal, wind and solar. Thanks to Brazil’s many rivers, hydro was historically a dominant energy source, but there has been a significant increase in the growth of wind and solar farms—ONS currently has over 220 wind and solar farms, and by 2029, 45% of its energy mix will be wind and solar.
While wind and solar are great renewable energy sources, they introduce tremendous operational challenges. Fluctuations due to variability in weather are hard to predict, and sudden changes can happen at any time. Consequently, operators must be ready to react quickly to ensure that demand meets supply and that generated clean energy doesn’t go to waste. Previously, ONS relied on a manual system of phone calls to coordinate this process, which was inefficient and often wasted precious energy.
So ONS created a solution that integrated AVEVA™ PI System™ with an energy management platform to provide real-time monitoring, forecasting, automation, and data-driven decision-making to optimize energy dispatch. By enabling faster adjustments, ONS achieved a 98% improvement in operational communication efficiency, saved 211 GWH of renewable energy (enough to supply San Francisco with energy for 15 full days), and avoided US$11.4 million in losses in 2024.

Ormat boosts geothermal output with predictive analytics
Geothermal energy is getting a lot of attention right now as a renewable energy source. Unlike solar or wind, geothermal provides constant power, 24/7. This makes it extremely valuable for grid stability.
The largest geothermal company in the world, Ormat, has been in business for 60 years. Ormat is unique for a geothermal company in that it is fully vertically integrated: it designs and operates its own plants that produce electricity; stores and sells electricity to the grid; and designs, builds and supplies power-generating equipment for customers’ geothermal plants.
To produce geothermal energy, Ormat must extract hot brine from the earth, process it for use, and then inject it back into the earth. This is a complex process that involves many moving parts. Real-time monitoring for each asset is fundamental for efficient operations. So Ormat is using AVEVA™ Plant SCADA and AVEVA™ Historian at the plant level, integrated into AVEVA PI System, to streamline data collection, access, analysis, and visualization.
Using an asset-based approach with AVEVA PI System’s Asset Framework, Ormat can standardize asset modeling, using templates for equipment such as generators, turbines, pumps, and heat exchangers. This way, Ormat is able to scale its monitoring solution across all sites. With easy visualizations, users can quickly check actual performance of equipment versus projected performance and perform advanced analytics, incorporating complex thermodynamic KPIs, for condition-based monitoring and predictive maintenance. In one instance, Ormat identified about 1MW potential additional generation due to repair of a cooling tower. Overall, the company projects an average of $1 million in added revenue per plant per year as a result of predictive maintenance.
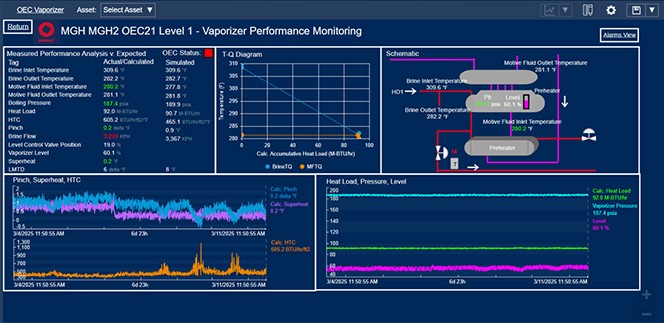 Dashboards allow Ormat to easily see expected versus actual performance of equipment.
Dashboards allow Ormat to easily see expected versus actual performance of equipment.
Renewable energy across the value chain with smart data management
Qair, an independent fully integrated renewable energy company based in France, is helping decarbonize European industry for the energy transition. The company is committed to making green energy available and affordable. In order to accomplish this, Qair designs, operates, and manages a diverse and growing mix of renewables: solar, offshore and onshore wind, battery storage, green hydrogen, and hydro power.
Qair uses AVEVA™ Process Simulation to optimize design of renewable plants and processes and ensure optimal asset sizing and cost efficiency. AVEVA Process Simulation also enables continuity from design to operations. Using AVEVA PI System and AVEVA™ InTouch HMI, Qair can visualize and analyze massive amounts of real-time production data. This data management platform sets the foundation for what the company sees as the key to success in the energy transition: communication between energy producers and energy consumers, communication that relies on reliable, precise, real-time data.
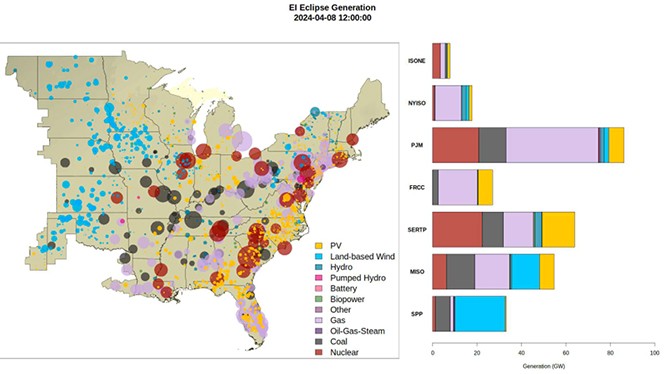 A possible future application of AI-powered grid management, looking at the ideal mix of renewable energy sources amid a solar eclipse.
A possible future application of AI-powered grid management, looking at the ideal mix of renewable energy sources amid a solar eclipse.
What’s next: The possibilities of AI and smarter grid management
New digital technologies such as AI, while often requiring the expenditure of energy, are positioned to significantly help the abatement of emissions from energy production. The World Economic Forum estimates that digital technologies could cut emissions by up to 20% by 2050.[3] And generative AI is leading the charge.
The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), for example, is exploring the use of digital twin technology and AI to more efficiently manage the grid. NREL has developed eGridGPT, an LLM that virtually assists system operators. eGridGPT integrates with AVEVA PI System and digital twin technology to offer operators, engineers, and corporate users enhanced guidance and decision support.
The operator can ask a question, a what-if, then a digital twin runs the simulation of the what-if, which the LLM orchestrates and then interprets, providing an answer or suggesting an action. NREL is currently in ongoing collaboration and development with vendors, utilities, and research institutions to improve and implement eGridGPt.
This kind of AI-guided operator assistance will likely continue to grow, with grid management becoming smarter and renewable energy more feasible. It's an exciting time for renewable energy producers and organizations that want to produce or use renewable energy (or both) for more cost-effective, sustainable operations. The future of renewable energy is bright—and getting smarter every day.
[1] Mengpin Ge, Johannes Friedrich and Leandro Vigna. (December 5, 2024). Where Do Emissions Come From? 4 Charts Explain Greenhouse Gas Emissions by Sector. World Resources Institute. https://www.wri.org/insights/4-charts-explain-greenhouse-gas-emissions-countries-and-sectors
[2] UNDP. (February 3, 2025). What is the sustainable energy transition and why is it key to tackling climate change? https://climatepromise.undp.org/news-and-stories/what-sustainable-energy-transition-and-why-it-key-tackling-climate-change
[3] World Bank Group. (November 29, 2023). Digital Technologies Fast Track Climate Solutions. https://www.worldbank.org/en/news/press-release/2023/11/29/digital-technologies-fast-track-climate-solutions
Related blog posts
Stay in the know: Keep up to date on the latest happenings around the industry.